Problem Description
Given a binary tree root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Example 1:
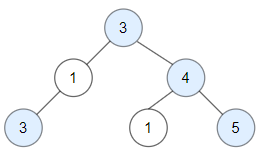
- Input:
root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5] - Output:
4 - Explanation:
Nodes in blue are good
Example 2:
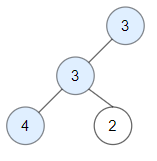
- Input:
root = [3,3,null,4,2] - Output:
3
My Idea
The idea here is to utilize a modified pre-order DFS, where at every step we also keep the current max value on the path, so we can make a decision on weather a node is good or not. This yields a time complexity of O(n).
My solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
# Time Complexity: O(n)
def goodNodes(root: TreeNode) -> int:
def traverse(node: TreeNode, m: int):
if not node:
return 0
res = 1 if node.val >= m else 0
m = max(m, node.val)
res += traverse(node.left,m)
res += traverse(node.right,m)
return res
return traverse(root,root.val)