Problem Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree’s maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:
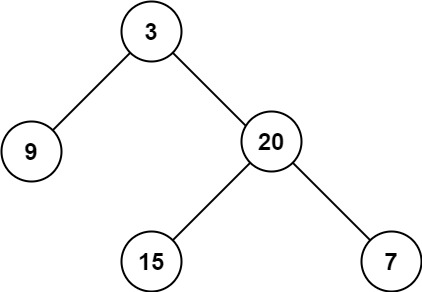
- Input:
root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] - Output:
3
Example 2:
- Input:
root = [1,null,2] - Output:
2
My Idea
My idea here was to utilize recursion and DFS. If the root has no children return 1, else return 1 plus the max from the depths of its children.
My solution
from typing import Optional
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
# Time Complexity: O(n)
def maxDepth(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if not root.left and not root.right:
return 1
return 1 + max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right))