Problem Description
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1:
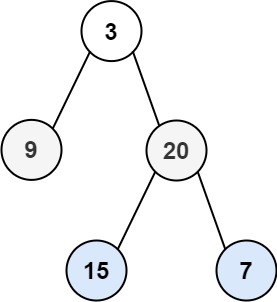
- Input:
root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] - Output:
[[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
Example 2:
- Input:
root = [] - Output:
[]
My Idea
The problem here is essentially implementing Breath First Search (BFS). To do this we need a queue. First we add the root node to the queue. Then while the queue is not empty we create a list for every lvl, which is essentially len(q) at the current iteration. Then for every one of the nodes at this current level, we dequeue it, add its value to the current level list and append its left and right children in this order to the queue. Once we’re done with this level, we append the resulting list to res and go on to the next iteration. As this is a traversal algorithm we have a time complexity of O(n)
My solution
from typing import Optional
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
# Time Complexity: O(n)
from collections import deque
def levelOrder(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
q = deque()
q.append(root)
while q:
lvl = []
l = len(q)
for _ in range(l):
curr = q.popleft()
if curr:
lvl.append(curr.val)
q.append(curr.left)
q.append(curr.right)
if lvl:
res.append(lvl)
return res